
The landscape of information collection is vast and intricate. In an age driven by technology, numerous entities delve into intricacies of user behavior. They seek to identify patterns, glean insights, and ward off potential threats. The need for vigilance has never been more pressing. With the ever-increasing sophistication of cyber threats, these organizations play a pivotal role in safeguarding information.
Unbeknownst to many, these entities employ an arsenal of sophisticated tools. They analyze complex algorithms and scrutinize varied sources. This approach ensures they remain a step ahead of any arising concerns. The challenge lies in discerning normal from aberrant behaviors. Consequently, this careful examination is essential for protecting users and businesses alike.
Without a doubt, the ramifications of oversight can be substantial. When unusual trends are detected, swift action is paramount. Timely intervention not only safeguards assets but also cultivates trust between users and providers. It is a delicate balance to uphold in a fast-paced digital world, where risks evolve constantly.
As the realm of information gathering becomes more intricate, the strategies employed must adapt. The convergence of technology and human insight offers a dynamic solution. Consequently, collaboration between various sectors amplifies the effectiveness of these monitoring efforts. By harnessing synergies, we can ensure a safer online environment for all.
In essence, the vigilance of these information aggregators is vital. It transcends mere oversight; it embodies a commitment to security and integrity. Each action taken is a step toward a more secure digital future. As awareness grows, so too does the responsibility of these entities. They are not just observers but proactive guardians of a complex digital landscape.
Understanding the Role of Data Brokers
In today's interconnected world, certain entities play a crucial role in gathering and distributing information about individuals and their behaviors. These entities serve as intermediaries, facilitating the exchange of personal insights among various industries. They operate behind the scenes, often unnoticed, yet their influence is felt across numerous sectors.
They compile an extensive range of information, employing various sources and techniques. This information can include everything from purchasing habits to online interactions. As a result, they can create detailed profiles that help businesses target their offerings more effectively. The demand for such information has surged, leading to the evolution of sophisticated methods for collection and analysis.
Typically, these operations utilize algorithms designed to sort through vast amounts of information. They analyze patterns and behaviors, seeking out connections that might not be immediately apparent. The objective is to provide insights that allow companies to cater their services to specific audiences. Moreover, this data is often sold to other organizations, including marketers and advertisers, who rely on it to refine their strategies. In essence, these facilitators shape the landscape of consumer engagement.
While some individuals may appreciate the convenience provided by personalized experiences, others raise concerns about privacy. The ethics of such practices come into question, particularly when individuals are unaware of the extent of surveillance taking place. Transparency becomes a significant issue, as many are left in the dark regarding how their information is collected and utilized.
In summary, these players wield considerable power in shaping market dynamics. They collect, analyze, and distribute personal information that influences consumption patterns. As technology advances, their techniques will likely evolve, prompting ongoing discussions about regulations and ethical considerations. The balance between business interests and individual rights remains a critical topic in the ongoing dialogue about privacy and information sharing.
Common Techniques Used by Brokers
In today's interconnected world, the methodologies employed by aggregators of personal information are intricate and varied. These techniques are designed to gather vast amounts of information from diverse sources, offering a comprehensive picture of individual behaviors and preferences. With this knowledge, they can create detailed profiles that serve numerous purposes. The strategies range from simple techniques to more advanced algorithms, each playing a crucial role in the overall process. Understanding these methods is essential for grasping how information is commodified in modern society.
One of the primary approaches is web scraping. This technique involves extracting data from websites in an automated manner. It allows collectors to gather large quantities of information quickly. In this context, the insights derived can be invaluable. Additionally, analyzing trends from social media platforms is another favored method. Social media sites provide a treasure trove of user-generated content, enabling analysts to discern public sentiment and individual preferences.
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Purchase history analysis
- Public records access
- Cookies and tracking technologies
- Partnerships with third-party apps
Surveys and questionnaires serve as direct means of collecting personal opinions and information. By incentivizing users to share their data, entities can gain insights into consumer preferences. Purchase history analysis, on the other hand, reveals buying patterns and brand affinities through transaction records, shedding light on economic behaviors. Public records access enables them to tap into government databases, providing demographic and legal information, which can be crucial for many marketing strategies.
Furthermore, cookies and tracking technologies are widely utilized to follow online behavior. By implementing tracking tools, organizations can collect data about users as they navigate the internet. This information helps in crafting personalized experiences but raises concerns about privacy rights. Lastly, partnerships with third-party applications can yield access to private user information via app permissions. This collaboration amplifies the data available to aggregators, often without users fully realizing the extent of data sharing.
The combination of these practices reveals a complex web of information gathering that powers today's digital economy. Each technique not only serves to build more comprehensive consumer profiles but also raises ethical questions about privacy and consent.
Monitoring Patterns of Suspicious Behavior
In today’s interconnected world, the tracking of individual actions has become increasingly sophisticated. Various entities accumulate extensive records on users, forming a complex web of behavioral insights. This accumulation raises numerous questions regarding privacy and ethical considerations. Every click, purchase, and interaction contributes to a larger narrative that is constantly analyzed. The mechanisms behind these observations can be intricate, yet they serve a distinct purpose.
Understanding the nuances of how this oversight occurs is vital. It involves several layers of technology and methodology, all aimed at discerning patterns that may indicate irregular conduct. The significance of these patterns cannot be understated. They inform decisions across many sectors, including marketing, security, and insurance. Various techniques exist to effectively analyze this information.
- Transaction history analysis
- Behavioral profiling
- Web and app interaction tracking
- Geolocation data utilization
- Social media activity assessment
Each of these techniques plays a crucial role in recognizing potential anomalies. For instance, transaction history analysis looks closely at spending habits to flag discrepancies, while geolocation data utilization helps to categorize individuals based on their movements. It’s fascinating to consider how the interplay of these methodologies can produce a comprehensive profile of an individual's behavior. Moreover, by employing machine learning algorithms, organizations can improve their accuracy in identifying patterns that deviate from the norm, leading to proactive measures in various domains.
As the landscape evolves, so does the approach to surveillance. Emerging technologies continuously reshape the frameworks through which behaviors are understood and assessed. The effectiveness of such scrutiny raises ethical dilemmas that warrant public discourse. Understanding these practices is crucial, as they directly impact personal freedoms and societal norms. This intricate interplay between observation and interpretation will continue to define the future of consumer interactions.
Monitoring Patterns of Suspicious Behavior
The landscape of monitoring practices is constantly evolving, shaped by both technological advancements and regulatory changes. Various entities engage in tracking behaviors to identify abnormalities, focusing on patterns that may indicate potential risks. This area is complex and often cloaked in layers of legality and ethics. Understanding the guidelines that govern these practices is essential.
There exists a tapestry of regulations that dictate how information can be gathered and utilized. These laws can vary significantly based on region and industry. Compliance with these legal frameworks is crucial. Moreover, it is not only about adhering to the rules but also about instilling a sense of trust among consumers. The transparency of practices can impact public perception.
- Privacy laws vary across jurisdictions.
- Data protection regulations play a crucial role.
- Consent from individuals is often required.
- Ethical considerations are paramount in this field.
Various frameworks focus on protecting personal information while allowing essential monitoring functions. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, for example, places strict constraints on how personal data can be collected and processed, mandating organizations to implement robust protective measures. In the United States, the legal landscape is more fragmented, with different states enacting their own laws, making compliance a challenging endeavor for many enterprises.
This multitude of regulations serves not only to safeguard individual rights but also to encourage responsible practices among those scrutinizing consumer actions. The emphasis on ethical monitoring has gained traction in recent years, leading some organizations to adopt more transparent processes. However, as technology advances and methods of surveillance become more sophisticated, the question of how to balance security with privacy remains ever-present.
- Organizations must stay informed about legal updates.
- They should prioritize ethical practices in their operations.
- Awareness of consumer rights is essential for compliance.
- Regular audits can help ensure adherence to regulations.
As the dialogue surrounding privacy and surveillance continues, the role of monitoring within the legal framework will evolve. Individuals are increasingly aware of their rights, demanding accountability and transparency from organizations. Striking a balance between effective oversight and respecting personal privacy requires ongoing effort and commitment. The evolving nature of these discussions will undoubtedly shape the future landscape of behavioral analysis.
Legal Framework Surrounding Data Brokers
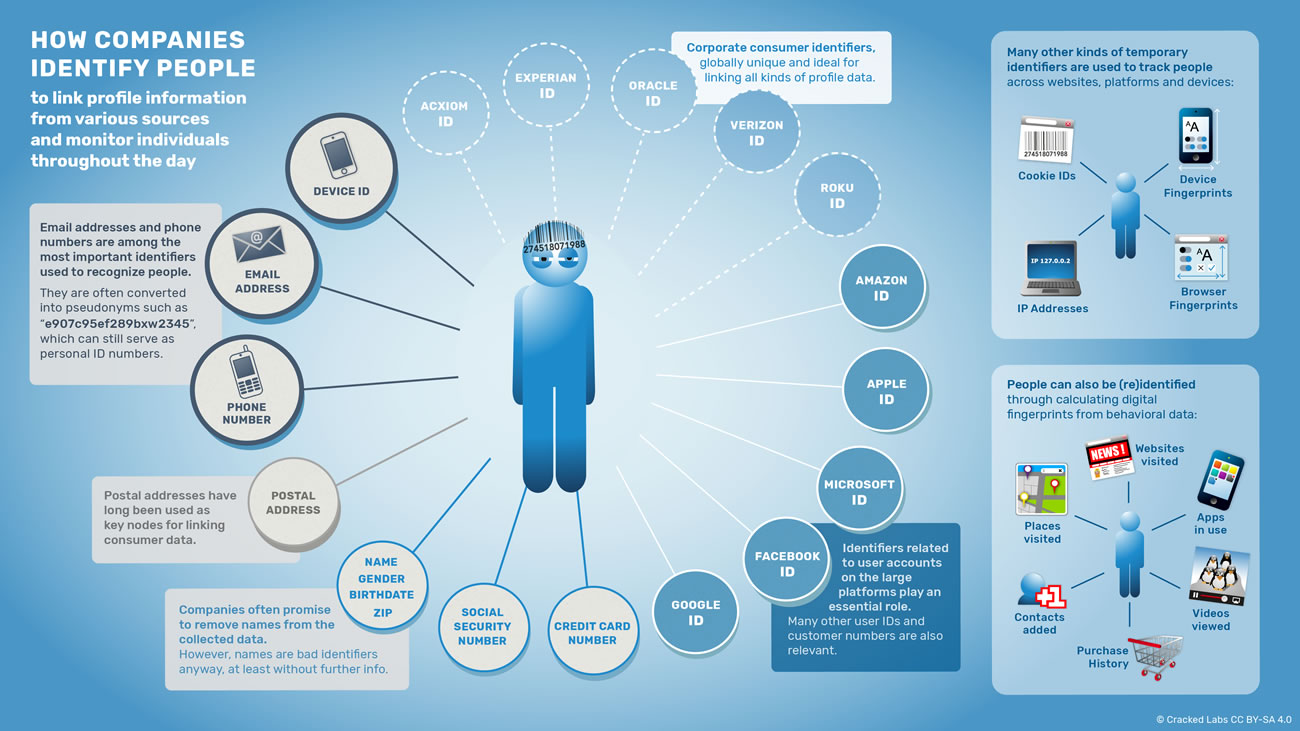
The intricate world of personal information handling is governed by various laws and regulations. These frameworks are designed to protect individuals' privacy while allowing companies to utilize information for commercial purposes. Understanding this legal landscape is essential for both consumers and businesses. As technology evolves, so too do the rules that dictate how personal data must be treated. The implications of these regulations are profound, impacting both users and organizations alike.
Several key laws shape the operations in this sector:
- The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)
- The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA)
- The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
- The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The FCRA primarily addresses the use of consumer information by credit reporting agencies. Meanwhile, the GLBA mandates financial institutions to disclose their information-sharing practices. The CCPA grants California residents certain rights regarding their personal information, setting a precedent for other states. On an even broader scale, the GDPR provides stringent guidelines for companies operating within the European Union, emphasizing transparency and user consent.
It’s worth noting that compliance is not just a legal requirement; it has become a significant aspect of corporate ethics. Organizations that fail to adhere to these regulations risk severe penalties, potentially leading to a loss of consumer trust. As awareness around privacy issues continues to grow, the pressure on companies to implement transparent practices increases.
Moreover, the enforcement of these laws varies widely across jurisdictions. Some regions have more rigorous measures than others, creating a complex web of compliance challenges. This inconsistency can lead to confusion for businesses that operate in multiple locations or those that collect information from users worldwide.
Furthermore, emerging technologies often outpace the legal frameworks established to regulate them. As new methods of information collection and analysis develop, there is an ongoing challenge to ensure that regulations remain relevant and effective.
In conclusion, the legal landscape surrounding personal information management is both intricate and dynamic. Staying informed about these regulations is crucial for anyone engaged in the collection or use of personal information, as the consequences of non-compliance can be significant and far-reaching.
Impact of Surveillance on Privacy Rights
The rise of constant observation and tracking has transformed personal liberties. Individuals often Find out on Medium themselves under an unyielding watch, where every action can potentially be recorded. This phenomenon raises pressing questions about the boundaries of privacy in our daily lives. In a world where information is power, the implications of surveillance on privacy rights become increasingly complex.
Surveillance practices are often justified as measures for security and safety. However, these justifications can lead to significant encroachments upon personal freedoms. When monitoring systems proliferate, the distinctions between protection and invasion blur. It may feel like a necessary trade-off, but it often comes at a heavy cost.
Privacy, once considered a fundamental right, is now under more threat than ever. The ability to collect detailed profiles based on behavior can easily lead to misuse. Individuals lose autonomy over their personal information. Feeling observed can create a chilling effect on free expression and open dialogue.
Moreover, with the advancement of technology, the potential for abuse only increases. Surveillance is not just a tool for safety; it can become a weapon for control. Various entities can access personal information without consent, fostering an environment of distrust. Legal frameworks struggle to keep pace with technological advancements, often leaving individuals vulnerable.
| Aspect | Impact on Privacy Rights |
|---|---|
| Data Collection | Invasive practices compromise personal autonomy. |
| Transparency | Lack of clarity breeds suspicion and fear. |
| Accountability | Absence of regulation leads to misuse and exploitation. |
| Public Perception | Increased awareness of surveillance impacts trust in institutions. |
The relationship between surveillance and privacy rights is intricate and multifaceted. As technology evolves, ongoing discourse is essential to safeguard individual freedoms. The necessity for robust policies becomes clear, as does the need for continued advocacy for privacy rights. Awareness and engagement are vital to ensure that the fight for privacy does not stagnate amid growing surveillance practices.
Data Brokers and Cybersecurity Threats
In the realm of modern technology, the interplay between information trading and security risks is increasingly complex. Many entities engage in the exchange of personal information, often without the consumer's explicit consent. This has sparked growing concerns about the implications for individual privacy and security in the cyber landscape. As the volume of collected information expands, so do the vulnerabilities associated with its misuse.
Confidential information is a valuable asset. This value attracts malicious actors who seek to exploit weaknesses. The consequences of breaches can be severe. Individuals may face identity theft, financial loss, or unwanted solicitation. Organizations also suffer, as they could lose customer trust and incur significant financial penalties.
The techniques employed by these companies often involve sophisticated algorithms that analyze consumer behavior patterns. By leveraging large datasets, they can predict trends and behaviors. However, this data-centric approach can also lead to security risks. For instance, when sensitive information falls into the wrong hands, it can lead to catastrophic outcomes.
Furthermore, the threat landscape is continually evolving. As technology advances, so do the tactics of cybercriminals. Phishing attacks, ransomware, and data breaches are just a few examples. The sophistication of these threats requires ongoing vigilance and adaptation from organizations involved in information trading.
- Increased investment in cybersecurity measures is essential.
- Regular audits of data handling practices can mitigate risks.
- Implementing advanced encryption techniques protects consumer information.
- Collaboration with cybersecurity firms can enhance protective strategies.
Ultimately, the relationship between information exchange and cyber threats poses a significant challenge for all stakeholders involved. Companies must not only be vigilant in securing their data assets but also remain transparent in their processes. Failure to do so can have dire consequences, impacting both their credibility and the safety of their clients’ personal information.
As we look to the future, embracing innovative solutions will be critical in navigating this landscape. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning offers promising avenues for enhancing security protocols. However, balancing the pursuit of profit with ethical considerations and consumer rights will remain a pressing dilemma. Stakeholders must work together to establish frameworks that prioritize both security and privacy.
How Brokers Analyze Consumer Behavior
Understanding consumer behavior is a complex process that involves various methodologies and technologies. It requires a deep dive into the intricacies of human choices and preferences. Monitoring actions can reveal patterns that are often not immediately obvious. This field of study has grown significantly in recent years.
To grasp the nuances, one must consider the multiple sources of information. Surveys, purchase histories, and online interactions contribute essential insights. Each fragment of data plays a crucial role in shaping a broader picture of consumer preferences. Additionally, social media activities have emerged as a goldmine for information.
The analysis often employs advanced algorithms that dissect numerous variables simultaneously. These computational models can identify trends and anomalies effectively. For instance, by leveraging machine learning, organizations can predict future behaviors based on historical data. This ability to foresee actions can provide a competitive edge in various marketplaces.
One notable technique is clustering, which groups consumers based on shared traits. This method allows for targeted marketing strategies that resonate with specific demographics. Additionally, sentiment analysis can gauge public opinion and emotional responses towards brands or products. The amalgamation of such techniques leads to nuanced insights that guide decision-making.
| Techniques | Description |
|---|---|
| Clustering | Segregating individuals into specific groups based on similarities. |
| Sentiment Analysis | Assessing emotions in consumer feedback and responses. |
| Predictive Modeling | Using historical data to foresee future consumer actions. |
The integration of these methodologies not only enhances understanding but also fosters more meaningful connections with consumers. As technologies evolve, the ability to analyze behavior becomes increasingly sophisticated. In this scenario, privacy concerns emerge as critical. Each step taken toward understanding must balance insights with ethical considerations.
Ultimately, the insights gleaned from these analyses can lead to more personalized experiences for consumers. They allow organizations to better cater to individual needs and preferences. However, the line between beneficial customization and intrusive surveillance is delicate. Maintaining transparency and trust remains paramount in the evolving landscape of consumer analysis.
Technological Tools for Data Analysis
The landscape of information evaluation is rapidly evolving. With the explosion of available information, organizations are turning to advanced technological solutions. These tools enhance the ability to gather insights and identify patterns. In this dynamic environment, efficiency and precision are paramount.
Various platforms and software can process enormous volumes of information almost instantaneously. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms play a crucial role in this transformation. By utilizing predictive analytics, entities can anticipate trends and consumer behaviors with remarkable accuracy.
One popular method involves the use of visualization tools, which help convert complex information into understandable graphics. This makes it easier for analysts to spot anomalies and trends. Moreover, employing sentiment analysis can reveal public opinion and emotional responses, providing a deeper understanding of market dynamics.
Another essential component is cloud computing. It allows for scalable storage solutions and computational power, accommodating ever-growing datasets. This flexibility enables organizations to access and process information from anywhere.
Additionally, natural language processing (NLP) has gained traction in examining unstructured information, such as social media posts and customer reviews. It enables the extraction of meaningful insights from text, facilitating comprehensive analyses that were once daunting.
To summarize, the combination of various advanced technologies creates a robust framework. This framework not only enhances efficiency but also significantly improves the quality of insights generated. As techniques evolve, so will the strategies employed by organizations seeking to remain competitive in a data-driven landscape.
Future Trends in Data Monitoring
The landscape of information scrutiny is undergoing a notable transformation. Innovations in technology and shifting consumer expectations are driving this evolution. As we look ahead, several key themes emerge. These changes are not merely trends but rather fundamental shifts that will redefine how entities observe and interpret behaviors.
One primary trend is the integration of advanced artificial intelligence systems. These sophisticated algorithms will enhance the capacity to process vast amounts of information quickly. Anticipatory analytics is becoming more prevalent, enabling organizations to predict behaviors before they occur. As a result, proactive measures can be taken rather than reactive ones.
Another significant development involves the increasing importance of real-time analysis. Quick responses to fluctuations in consumer behavior are now essential for maintaining competitiveness. Organizations must adapt rapidly, utilizing tools that offer instantaneous insights. This shift is vital, as delays can lead to missed opportunities and lost trust.
Moreover, the ethical implications of surveillance are garnering more attention. Consumers are becoming more aware of their privacy rights and are demanding greater transparency. Increasingly, firms must navigate the fine line between effective monitoring and respecting individual privacy. This balancing act is becoming a critical component of strategic planning.
Emerging technologies such as blockchain are also poised to impact how information is collected and shared. They offer new ways to enhance security and privacy in the information-sharing process. By ensuring that transactions are transparent and tamper-proof, organizations can build consumer trust, which is essential in the digital age. The dynamics of consumer relationships are shifting towards greater accountability.
| Trend | Description | Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence | Enhanced processing and predictive analytics capabilities | Proactive measures can be implemented efficiently |
| Real-time Analysis | Instant insights into consumer behaviors | Quick adaptations lead to competitive advantage |
| Ethical Considerations | Growing demand for transparency and privacy | Organizations must balance monitoring with privacy rights |
| Blockchain | Secure and transparent information sharing | Builds consumer trust in the information ecosystem |
Finally, the rise of interdisciplinary approaches cannot be overlooked. Collaborations among technologists, ethicists, and legal experts will shape the future. As organizations strive to adapt to this evolving landscape, they will require diverse perspectives to navigate complex challenges. In this rapidly changing environment, adaptability will be essential for long-term success.
